
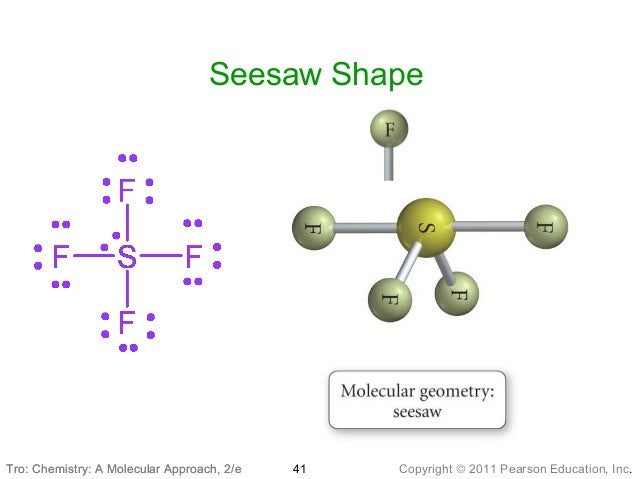
So we can move a lone pair from each oxygen, to form two double bonds between C The central carbon only has a share in 4 valence electrons, What is the Lewis structure of carbon dioxide, CO 2? There are 16 valence electrons to work It will have a linear geometry, because there are two groups (the two Cl atoms) separated in space. The central atom, Be, has two pairs of bonding electrons. This is a molecule with fewer than 8 valence electrons. What is the Lewis structure of BeCl 2 ? Be has 2 valence electrons, and each ClĬontributes 7 valence electrons, for a total of 16 electrons. With 90 obetween all of the valence electrons. The groupsĪbove and below the central triangle are at a 90 o angle to the triangle.Įlectrons separated in space will form an octahedron, This shape consists of a triangle with two electron pairsĪngles of the middle, triangular portion are 120 o.

The bond angle in a tetrahedron is 109.5 o. The bond angle in this structure is 120 o.Īre separated as far as possible from each other. The angle between the lone pairs and the central atom is 180 o.Įlectrons pairs get as far apart from each other, a trigonal planar structure is formed, as shown below.
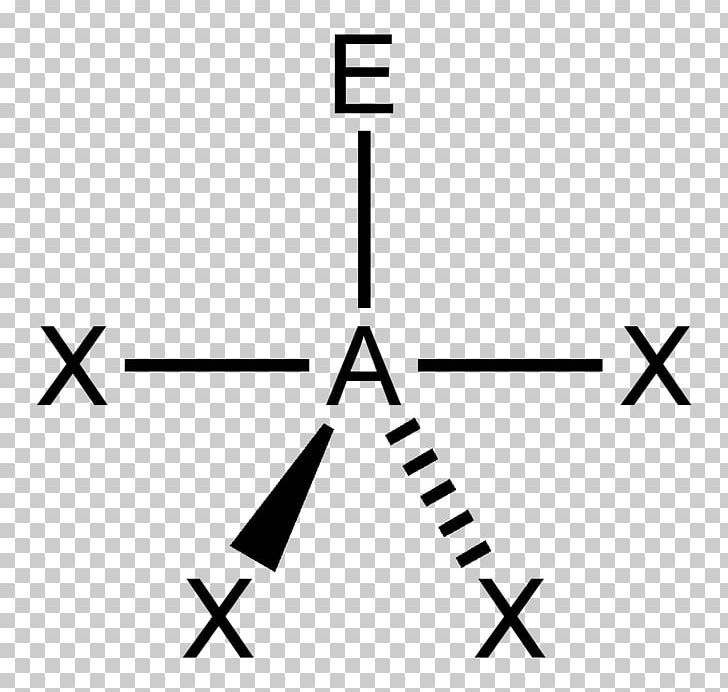
The pairs of dots ( :) represent two pairs of valenceĮlectrons forming bonds to the central atom. Try to get as far away from each other as possible, a linear shape is formed. These electron pairs will keep as far away from each other, due to The concept is that valence shell electron pairs are involved in bonding, and that Lewis structures can give us an approximateĪ simple procedure that allows us to predict overall geometry is the VSEPR, Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion. The bond lengths and angles, are determined experimentally.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
